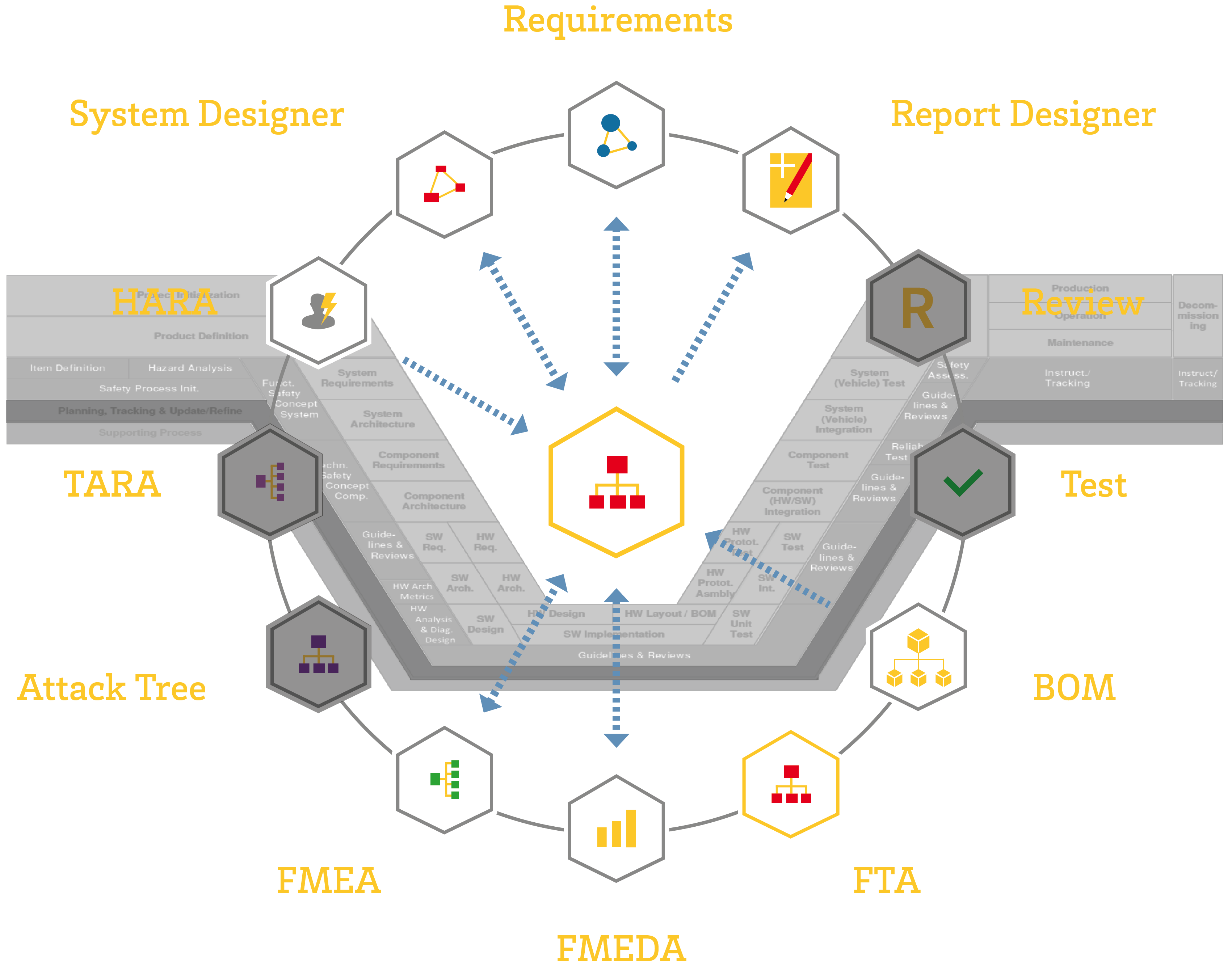
EnCo SOX FAULT TREE ANALYSIS
Optimize your Fault Tree Analysis, Enhance multi-user Collaboration, and Ensure Compliance with DIN 25424 and IEC 61025 Standards.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Optimized Fault Tree Modeling and Analysis
Seamless Integration
Advanced Probability Calculations
Customizable Reporting
Enhanced Documentation
Modular Design
In the Requirements module, you can create or edit requirements which can then be used in your FTAs. All changes, results, connections or relations will then also be visible in all of your requirements thanks to the full tracesbility features of the SOX workbench.
Requirements
- Supports OMG standard ReqIF exchange format and import of MS Office
- Deep integrations with IBM Doors, Codebeamer, Jama Connect, Jira, and Polarion
The SOX Requirement module offers a complete solution for elicitation, tracking and analyzing requirements. Import your product requirements specifications from Excel, Word, ReqIF or Rif and create the specification document in SOX. For this, you can reuse data former projects from the server-based catalog, compare different concepts and make status alignments via the SOX Traceability Matrix.
Display your FTA data within dedicated Safety- and Security Reports.
Report Designer
The SOX Report Designer helps you create customized documentation for your projects with just a couple of clicks. Drag-and-drop data from existing projects and working files into your reports for seamless visualization and benefit from safety-and-security-focused live updates so your reporting is always in line with your most current data.
Review
- Definition of rules and queries
- Definition of the document status
- Generation of Review documents
Test
- Definition of test cases
- Export of test cases
- Import and display of test results
Create test cases based on your requirements in SOX and pass them to their specific testing tools. Please approach us for specific data outputs. We will adjust the output in XML so you can pass SOX test cases along to your test tools and read back the status, so as to generate maximum assistance in the preparation of your project-related traceability.
BOM
- Linkage to the SOX modules FMEA, FTA, Markov, and RBD
- Standard catalogs of failure rates: SN 29500, IEC 62380
- Standard catalogs of failure modes: Birolini, IEC 62380
Import or create your Bills of Materials (BOMs) in the SOX Reliability module. FIT values are calculated in the SOX RE module in compliance with project-specific profiles and can be used for various analyzes.
SOX also enables the semiquantitative analysis from semiconductors down to their parts (DIE and Package) and sub-areas (Blocks), according to ISO26262 (part 11) and ISO PAS 19451.
Adopt Failure Modes from the BOM into the FTA
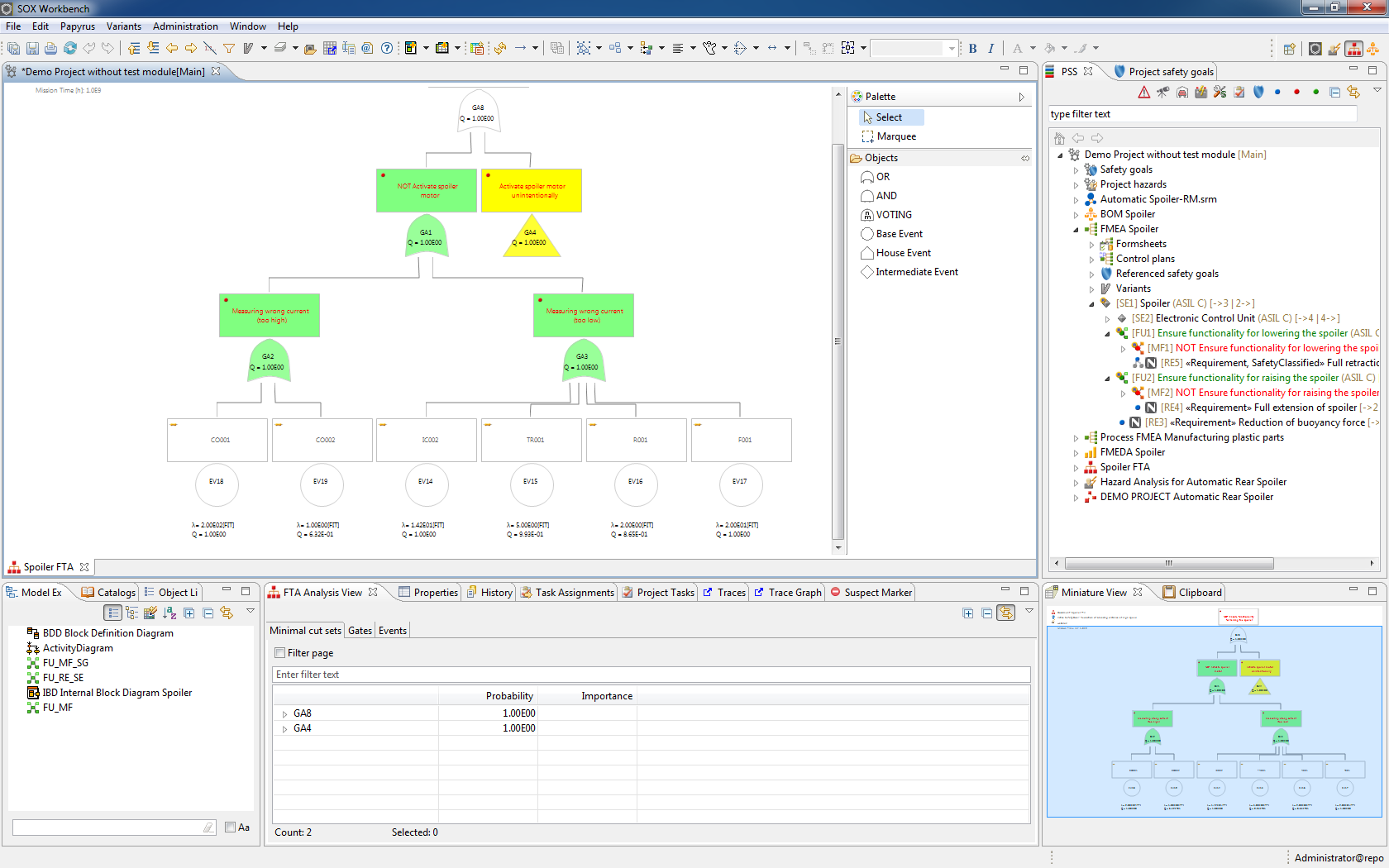
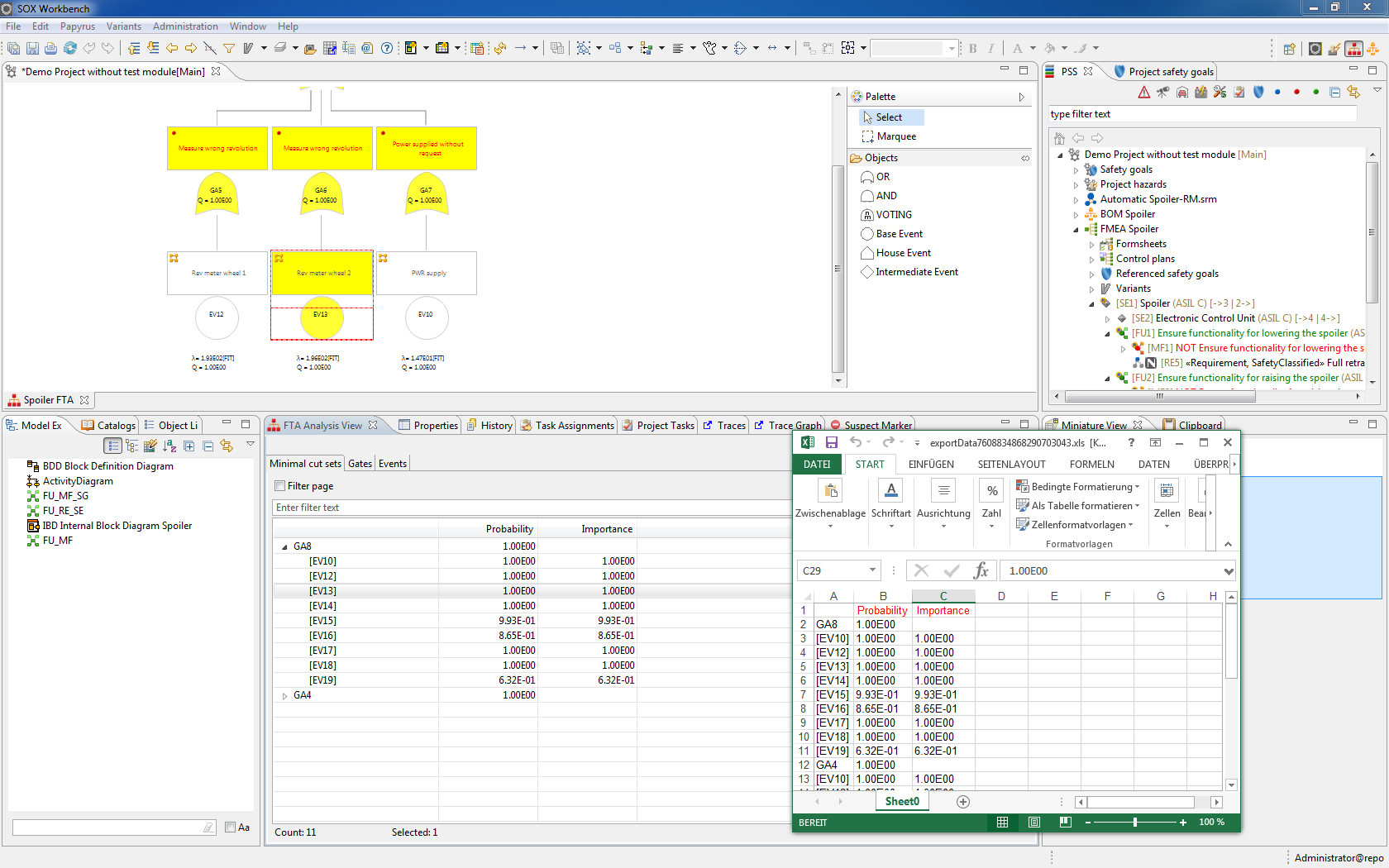
FTA
- Supports the standards DIN 25424 and IEC 61025
- Boundary value analysis and minimum intersection analysis
Calculate required probabilities in the SOX module FTA and track the progress of your analysis with the possibility to consign a status and to assign tasks. As an FTA software, the SOX module FTA provides the possibility, besides the option to display variants, to take over hardware and system effects of the FMEA or failure modes from the FMEDA and to link them simply by drag & drop. Sources and effects of risks are therefore systematically identified and eliminated with appropriate countermeasures (e.g. diagnoses).
FMEDA
- Supports Safety standards IEC 61508 and ISO 26262
- Analysis on module, component and semiconductor level
The SOX FMEDA supports you in creating FMEDAs for industry-specific safety standards (e.g. ISO 26262, IEC 61508). Calculate your safety target specific metrics for each module and the overall system in the SOX module FMEDA and track the progress of your analysis with the possibility to consign a status and to assign tasks.
SOX also enables the quantitative analysis from semiconductors down to their parts (DIE and Package) and sub-areas (Blocks), according to ISO 26262
Learn More
Use calculated FIT values from the FMEDA in the FTA.
FMEA
- Structure of FMEA according to VDA 6.3 & AIAG (7 steps method)
- Tracing and display of safety requirements (e. g. SIL, ASIL, PL)
- Connection to the SOX module Requirements (RIF / ReqIF) and System Design (SysML / UML)
- XML MSR FMEA and Excel Import
The SOX FMEA supports in risk analysis according to VDA & AIAG. One of the many unique selling points is to analyze electronic components professionally. Besides the option to display variants the SOX module, FMEA provides the possibility to define error nets and measures, depending on the system status (development, operation, service). Sources and effects of risks are therefore systematically identified and eliminated with appropriate countermeasures.
Automatic synchronization data between FTA and FMEDA. Adopt Hardware and System Effects & Adopt Failure Modes & Derive Failure Net Structures.
Attack Tree
- Taking threats from the TARA via Drag & Drop
- AND- & OR-Gates
- Customizable variables representing the probabilities of an Asset Attack
The SOX Attack Tree module makes graphical representations of attack paths available, providing Attack Goals, Attack Objectives, Attack Methods, and Asset Attacks and connects them with the responding AND and OR gates. Beyond the usual entities, Undeveloped Events and Transfers, referencing repeated nodes in different attack paths can be created.
TARA
- Allocates and rates threats which based on cyber attacks amongst other things
- Evaluates risks in accordance to the norm ISO/SAE 21434 and the guidebook SAE J3061
- TARA generation based on your previous UML/SysML system design
The SOX TARA allows the allocation, management and evaluation of assets, effects, threats, operating conditions and security attributes. The evaluation matrix facilitates the individual assembly of different security level reviews. Selected aspects can be filtered, sorted and viewed in a variety of configurations.
HARA
- Support for ISO 26262, IEC 61508, ISO 25119, ISO 12100/14121 MRL, MIL-882, ISO 13849, ISO 62061 and ISO 61511
- Server-based catalogs and document filing
- Analysis of hazards and safety requirements (safety goals)
The SOX module Hazard and Risk Analysis (HARA) evaluates your security needs and allows you to assemble various safety reviews (SIL, ASIL, PL, etc.), allowing you to allocation, manage, and evaluate functions, malfunctions, effects, hazards, operating conditions, and safety objectives. The evaluation matrix facilitates the individual assembly of different ASIL reviews. Selected aspects can be filtered, sorted and viewed in a variety of configurations.
Use more SOX modules to hand over defined security requirements to the SOX System Design (SysML / UML), the security concept modeling (FSK / TSK), requirements management (RIF, ReqIF) or SOX Analysis
The safety levels calculated in the HARA module are automatically transferred to the quantitative and qualitative analyzes (FMEA, FMEDA, FTA).
System Designer
- Supports OMG SysML / UML standards
- Import and export options to existing solutions via XMI (e.g. Enterprise Architect)
- Connection to the SOX module Requirements (RIF / ReqIF)
The SOX System Designer represents a comprehensive solution for modeling your specific system using the OMG SysML 1.6 and UML 2.0 standards. Define your system using a variety of chart types and link it based on specific requirements which can be passed into the SOX module Requirements.
Create System Elements, Functions, and Malfunctions